CT Scan
What is a CT Scan?
Computerized tomography (CT scan or CAT scan) is an X-ray technique that enables viewing of organs that cannot be seen with conventional X-rays.
While a conventional X-ray will show your bones and subtle outlines of other organs, CT images will reveal the bones and organs with a high degree of precision. A conventional X-ray uses a stationary machine to focus beams of radiation on a specific part of your body; a CT scan uses an X-ray generating device that rotates around your body and a powerful computer to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the inside of your body.
Preparing for a CT scan
Preparation for your CT scan depends on which part of your body will be scanned. Some scans, such as abdominal and pelvic, require a liquid contrast medium – usually a liquid such as barium or iodine – that is ingested or injected prior to your exam. The contrast medium helps differentiate structures or fluids within your body. If you are scheduled for a CT scan of the abdomen and/or pelvis, you may be asked to arrive before appointment time for contrast prep.
You can eat a normal diet and take daily medications; however, depending on the body area being scanned, your doctor may ask you to temporarily modify your diet, take laxatives, enemas or suppositories.
If you are receiving contrast during your exam, please consider the following:
- You can take your usual medications with water, but do not eat anything for at least four hours before your test. You may have clear liquids for four hours prior
- If you are on Glucophage (Metformin), you should take your morning dose and you should see your doctor for a blood test before taking Glucophage again
- Contrast medium can be difficult for some individuals to receive during the exam. We will ask a series of questions at the time of scheduling and at the time of the exam to ensure the patient is properly screened before receiving contrast
- With a contrast medium, although it is rare, there is a slight risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast. Most reactions result in itchiness or hives. If you have allergies or asthma, there is a slight risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast medium. In very rare instances, an allergic reaction may cause swelling in your throat or other areas of your body. Diabetes, heart disease, kidney problems or thyroid conditions also increase your risk of reaction to the contrast medium. Tell your technologist or doctor immediately if you experience any of these symptoms during or after your exam. Our staff and physicians are prepared should any type of emergency situation occur.
You may be asked to remove your clothing and put on a hospital gown.
You will be asked to remove all metal or electronic objects from your body before the exam as these objects interfere with the quality of the images.
For your safety
CT scan risks are similar to those of conventional X-rays. Unlike a magnetic resonance imaging scan (MRI), a CT scan can be performed if you have a pacemaker.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or suspect you may be pregnant. Your doctor may suggest an alternative exam that doesn’t require radiation, such as an MRI or ultrasound.
Please note: Parents will not be allowed to remain in the CT room with children who require sedation.
What to expect during a CT scan
CT scans are painless. You can expect your scan to last no more than an hour depending on the required preparation and whether a contrast medium is used.
Our technologist will prepare and guide you by explaining the procedure and positioning you to ensure the highest-quality images are obtained from your exam.
You may feel a brief sensation of heat or experience a metallic taste in your mouth if an intravenous (IV) contrast medium is used. If an enema is used to administer contrast, typically for gastrointestinal exams, you may feel cramping or a sense of fullness.
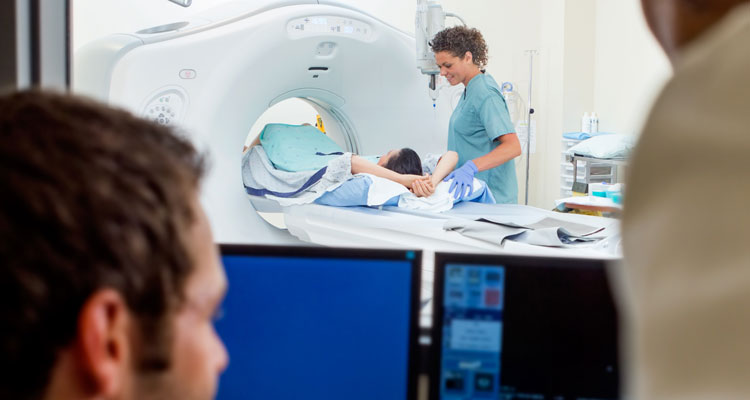
You will lie on a narrow table that slides through the opening of a large device called the gantry. The table can be raised or lowered. A special head cradle, pillows or straps may be used to help you remain in position.
The table will move slowly through the gantry as the X-ray tube rotates around your body. You may be asked to hold your breath while the table is moving to avoid blurring the images. You will hear noises similar to a small airplane or spinning clothes dryer as the X-ray rotates to create images of your body.
The technologist supervises the CT scan from a control room and can always see and hear you. An intercom is used to communicate.
When your exam is complete, you can leave and resume regular activities based on your doctor’s instructions. If you received a contrast medium, you will be given instructions to help remove the medium from your body. This will likely include drinking lots of fluids.
Our staff and physicians are prepared should any type of emergency situation occur.
Results
A radiologist will review your exam images and report the findings to your doctor. Your doctor will then discuss the findings and next steps with you.